Supply Chain Resilience, Rooted in Nature
DeepRoots AI designs and delivers nature-based interventions across your suppliers - strengthening resilience while enabling scalable regeneration that protects both nature and supply security.
PLATFORM OVERVIEW
Supply Chain Intelligence Built for Action
Combine satellite data, soil analysis, climate models, and market intelligence to generate farm-specific recommendations. Self-service platform, expert support when you need it.
Supply Chain Mapping
Visualise climate vulnerability across your entire supplier network
AI Recommendations
Farm-specific intervention strategies based on soil, climate, and market data
Financial Modeling
ROI projections, subsidy matching, and funding pathway analysis
Boost Farmer Engagement
Support farmers in transitioning to profitable, sustainable land use at scale
How the Platform Works
DeepRoots aligns farmer priorities, supply-chain needs and environmental data in one place. With instant AI-generated plans and coordinated delivery, you can move from ambition to execution across hundreds of farms with confidence and consistency.

A frictionless start for every farmer
Farmers enter a few basic details, including their SBI number, and immediately access the platform. No complex forms, no lengthy setup. This rapid time-to-value is designed to maximise engagement across large and diverse supplier networks.

Automated geospatial insight meets farmer context
DeepRoots automatically pulls in geospatial and environmental context from trusted third-party sources. Farmers can then add their business, financial and environmental goals, along with any preferred regeneration approaches. The platform builds a robust, nuanced picture of each landholding within minutes.

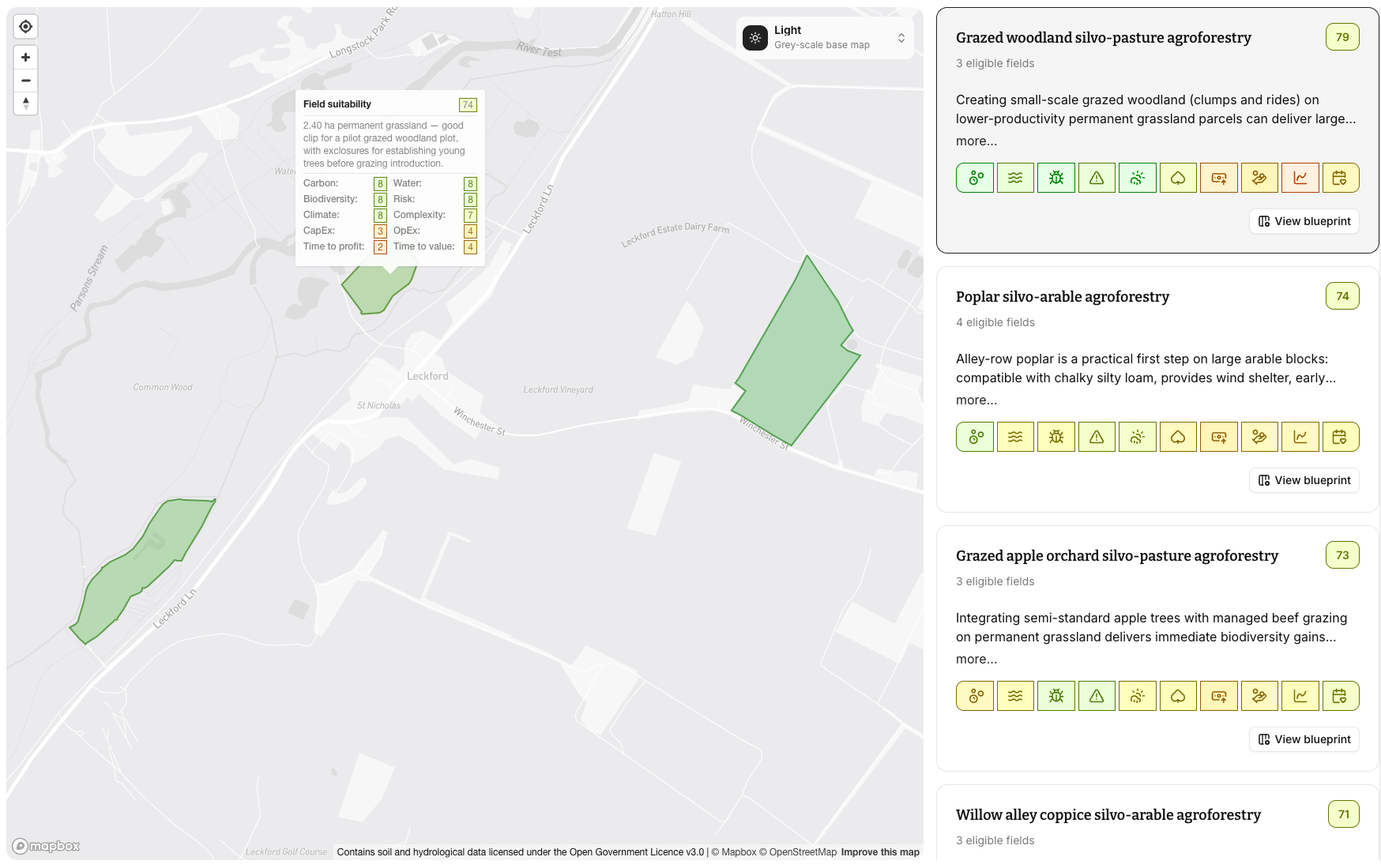
Scientifically-grounded, supply-chain-aligned interventions
The platform hosts a library of rigorously validated land-regeneration blueprints, from agroforestry systems to other nature-based interventions; created with industry experts and trusted partners. Tailored blueprints can be developed for specific categories or supply chains (e.g., cocoa, berries, livestock systems).

Farm-specific, future-ready regeneration plans
Our AI engine combines geospatial data, farmer inputs and supply-chain priorities to generate tailored regeneration recommendations. Each land parcel is evaluated for suitability, helping identify precise opportunities that strengthen resilience, improve yields and align with corporate nature targets.

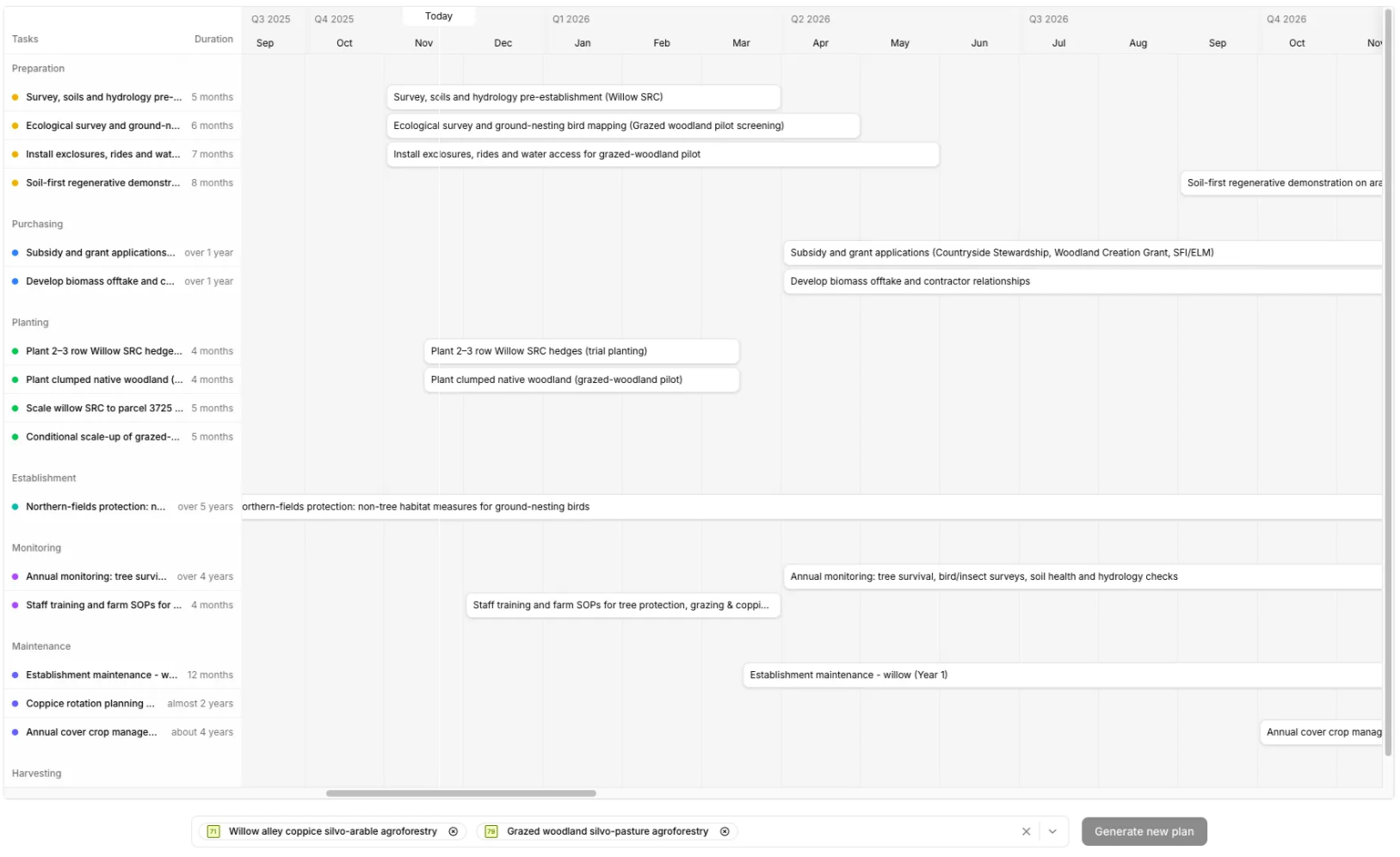
From recommendation to a deployable plan
Farmers select the opportunities they want to pursue. DeepRoots instantly generates a multi-year implementation roadmap; tailored to crop rotations, seasonality, financial constraints and policy opportunities. Every step is designed to be practical, achievable and commercially grounded.

Turning plans into real-world outcomes
Through DeepRoots’ network of trusted partners, farmers can get hands-on support to install and manage regeneration projects. This ensures interventions are delivered accurately, at scale, and in line with supply-chain objectives — turning digital insight into measurable impact.
Bring Real Regeneration to Your Supply Base
See how DeepRoots’ AI-driven planning and coordinated delivery can enhance supply security and reduce climate risk.